Headline
Meet Nigeria’s First Black Female President Of Harvard Law Review
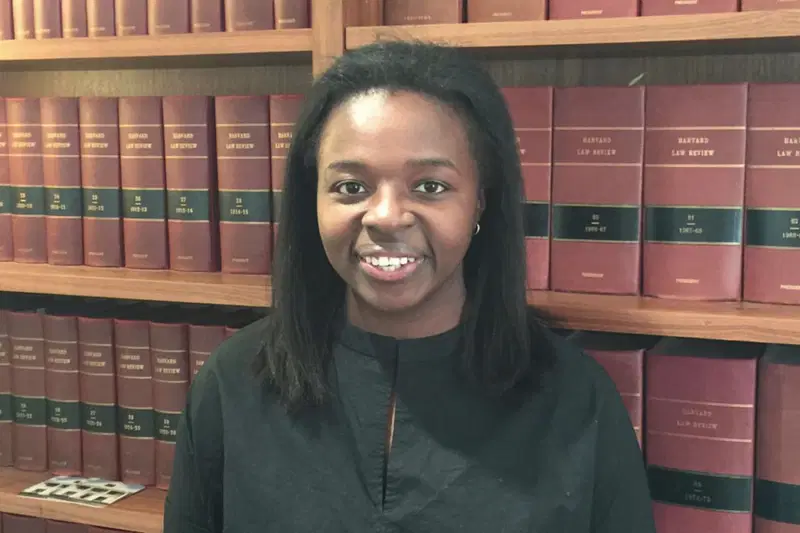

It took 27 years after Barack Obama became the first Black president of the Harvard Law Review for another milestone to be reached, this time, with a Black woman at the helm.
In 2017, ImeIme Umana made history as the first Black female president of the prestigious 130-year-old journal, a role regarded as one of the highest student positions at Harvard Law School.
Born to Nigerian parents in Pennsylvania, USA, Umana grew up as the third of four daughters in a family that valued education and resilience. Her late father worked as a statistician, and her upbringing instilled in her a strong sense of purpose.
Graduating from Harvard College in 2014 with a degree in Government and African-American Studies, she pursued her passion for law at Harvard Law School. But her journey to the top of the Law Review was no small feat, it required immense dedication, intellectual rigour, and a commitment to justice.
READ ALSO: Meet 36-Year-old Okolo, First Black Woman To Earn PhD In Aerospace Engineering
Making history in a male-dominated space
The Harvard Law Review is one of the most influential legal journals in the world, often shaping discussions on critical legal issues. It has served as a launching pad for many prominent figures in the legal field, including Supreme Court justices. However, for over a century, it was predominantly led by white men.
Umana’s election as the 131st president was groundbreaking. She was chosen by a vote of the Review’s 92 student editors after a rigorous selection process.
Championing diversity and justice
Umana’s legal philosophy is deeply rooted in her identity as a Black woman. She has been vocal about the systemic inequalities in the legal system, particularly how it disproportionately affects Black women. Reflecting on cases like those of Sandra Bland and Natasha McKenna, she expressed a strong commitment to fighting for justice.
Unlike many of her peers who opt for high-paying corporate law firms, Umana set her sights on public service. Her internship at the Bronx public defender’s office was a defining moment, reinforcing her desire to advocate for marginalized communities.
READ ALSO: Meet Nigerian Neurotech Who Built Computer That Can Smell Explosives
“A lot of the clients I worked with that summer and since have looked a lot like me,” she said. “They are disproportionately represented on the unfortunate end of the legal system, so it struck a little closer to home.”
After graduating, Umana secured a prestigious clerkship with Judge Robert L. Wilkins of the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit. She has remained steadfast in her goal to become a public defender, using her legal expertise to champion the rights of underprivileged individuals.
Ruth Okediji, a Harvard Law graduate and professor, praised her for her selflessness. “ImeIme was not just looking out for herself. I always tell my mentees; ‘You are not successful until you have brought the next woman up.’ And ImeIme has done just that.”
As a trailblazer, Umana’s story is one of perseverance, intellect, and a relentless pursuit of justice. She continues to inspire a new generation of Black women in law, proving that barriers can be broken and that representation matters.
Headline
Africa Coups: 10 In Five Years
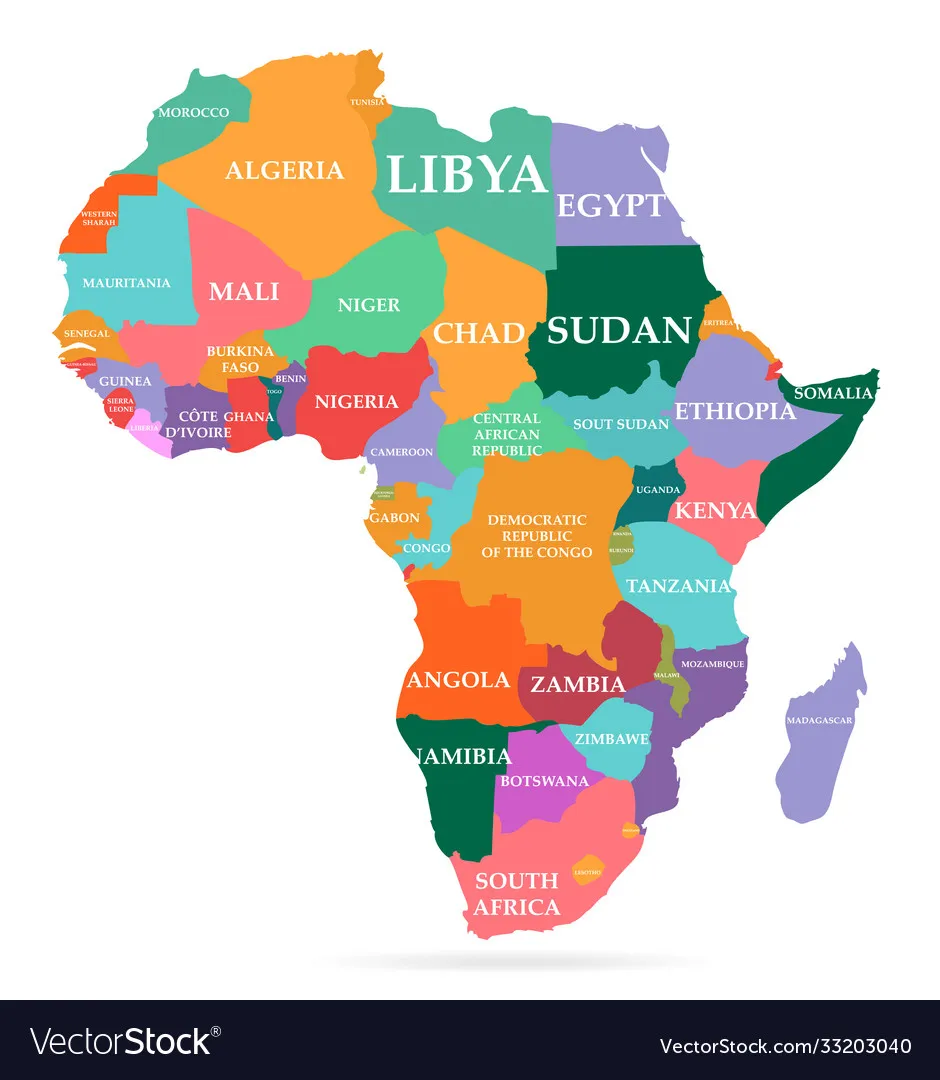
A military coup attempt in Benin Sunday adds to a list of such incidents on the turbulent African continent.
A group of soldiers announced that they had ousted President Patrice Talon, although his entourage said he was safe and the army was regaining control.
Here is a recap of the 10 successful coups in Africa in the last five years:
Mali
Malian President Ibrahim Boubacar Keita is overthrown by five army colonels in August 2020.
In May 2021, the Malian military takes over from the civilian leaders of an interim government.
Colonel Assimi Goita, who led both coups, is sworn in as transitional president.
After promising to hold elections in February 2024, the military puts them off indefinitely, pointing to the jihadist violence plaguing the country.
READ ALSO:Guinea-Bissau Military Takeover Is ‘Ceremonial Coup’ – Jonathan
In July 2025, Goita approves a law granting himself a five-year presidential mandate, renewable without election.
In September jihadists launch a fuel blockade, weakening the ruling junta.
Guinea
On September 5, 2021, mutinous troops led by lieutenant-colonel Mamady Doumbouya take over in Guinea, arresting President Alpha Conde.
Doumbouya in early November 2025 submits his candidacy ahead of December 28 elections that are meant to restore constitutional order.
Sudan
After weeks of tension between the military and civilian leaders who had shared power since the ousting of dictator Omar al-Bashir, the armed forces led by army chief Abdel Fattah al-Burhan stage a new coup on October 25, 2021.
Since April 2023 war has raged between the regular armed forces led by Burhan and the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces, led by his former deputy Mohammed Hamdan Daglo.
READ ALSO:Guinea-Bissau Coup: FG Gives Update On Ex-President Jonathan
The conflict has so far killed tens of thousands of people and created one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises.
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso underwent two military coups in 2022.
In January that year mutinous soldiers led by Lieutenant-Colonel Paul-Henri Sandaogo Damiba arrest President Roch Marc Christian Kabore.
Then in September army officers announce they have dismissed Damiba. Captain Ibrahim Traore becomes transitional president, but elections he promised do not materialise. In May 2024 the junta authorises him to stay for another five years in a country wracked by Islamist violence.
Niger
On July 26, 2023, members of the presidential guard overthrow Niger’s President Mohamed Bazoum, elected in 2021. General Abdourahamane Tiani, head of the presidential guard, takes over.
In March 2025, the junta extends by at least five years its transitional leadership of the country which is plagued by jihadist violence.
READ ALSO:Coup In Guinea-Bissau? Soldiers Deployed Near Presidential Palace After Gunfire
Gabon
In Gabon, ruled for 55 years by the Bongo family, army officers on August 30, 2023 overthrow President Ali Bongo Ondimba, less than an hour after he is declared winner of an election the opposition says was fraudulent.
General Brice Oligui Nguema is named transitional president.
In April 2025 he is elected president with 94.85 percent of the vote. He is sworn in on the basis of a new constitution approved by referendum during the transition.
Madagascar
In October 2025, the military ousts Madagascar’s president Andry Rajoelina and takes power following weeks of “Gen Z” anti-government protests.
Army colonel Michael Randrianirina is sworn in as Madagascar’s new president, promising elections within 18 to 24 months.
Guinea-Bissau
In November 2025, military officers in Guinea-Bissau declare they have “total control” of the coup-prone west African country, closing its borders and suspending its electoral process three days after general elections.
The military says a command “composed of all branches of the armed forces” is taking over the leadership of the country “until further notice”.
Headline
Benin Republic Presidency Breaks Silence On ‘Military Takeover’
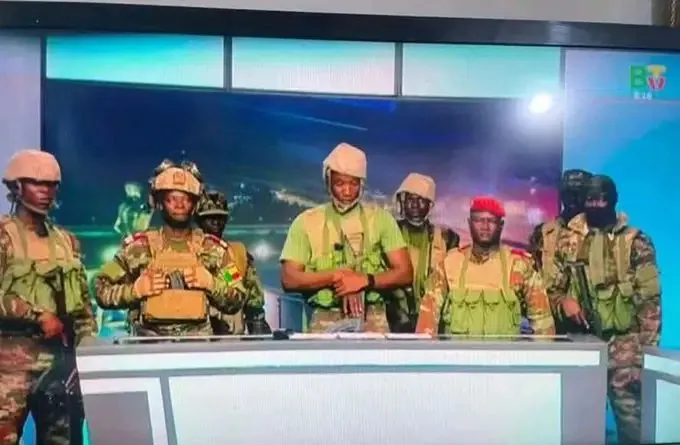

Benin Republic military
Military personnel in Benin on Sunday said they had ousted President Patrice Talon, but the Presidency said he was safe and the army was regaining control.
Talon, 67, a former businessman known as the “cotton king of Cotonou,” is due to hand over power in April next year after 10 years in office marked by strong economic growth and rising jihadist violence.
West Africa has seen several coups in recent years, including in Niger, Burkina Faso, Mali, Guinea, and most recently Guinea-Bissau.
Early on Sunday, soldiers calling themselves the “Military Committee for Refoundation” (CMR) said on state television that they had met and decided that “Mr Patrice Talon is removed from office as president of the republic.”
READ ALSO:Guinea-Bissau Military Takeover Is ‘Ceremonial Coup’ – Jonathan
The signal was cut later in the morning.
Shortly after the announcement, a source close to Talon told AFP the president was safe.
“This is a small group of people who only control the television. The regular army is regaining control. The city (Cotonou) and the country are completely secure,” they said.
“It’s just a matter of time before everything returns to normal. The clean-up is progressing well.”
A military source confirmed the situation was “under control” and said the coup plotters had not taken Talon’s residence or the presidential offices.
READ ALSO:Coup: ECOWAS Suspends Guinea-Bissau
The French Embassy reported on X that “gunfire was reported at Camp Guezo” near the president’s official residence in the economic capital and urged French citizens to remain indoors.
Benin has a history of coups and attempted coups.
Talon, who came to power in 2016, is due to end his second term in 2026, the constitutional maximum.
The main opposition party has been excluded from the race to succeed him, leaving the ruling party to compete against a so-called “moderate” opposition.
Talon has been praised for driving economic development but is often accused of authoritarianism.
(AFP)
Headline
JUST IN: Soldiers Announce Military Takeover Of Govt In Benin Republic

A group of soldiers appeared on Benin’s state television on Sunday to announce the dissolution of the government in what is being described as an apparent coup, marking yet another power seizure in West Africa.
Identifying themselves as the Military Committee for Refoundation, the soldiers declared the removal of the president and all state institutions.
READ ALSO:Guinea-Bissau Military Takeover Is ‘Ceremonial Coup’ – Jonathan
President Patrice Talon, who has been in office since 2016, was scheduled to leave office next April after the presidential election. His party’s preferred candidate, former Finance Minister Romuald Wadagni, had been widely viewed as the frontrunner. Opposition candidate Renaud Agbodjo was disqualified by the electoral commission on the grounds that he did not have “sufficient sponsors.”
The takeover comes a month after Benin’s legislature extended the presidential term from five to seven years while retaining the two-term limit.
(AFP)

 Metro2 days ago
Metro2 days agoEdo: How Pastor Hypnotised My Daughter, Made Her Abandoned NNPCL- Mother

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoEdo Assembly Recalls 324 Employment Letters

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoImansuangbon Donates To Benin IDPs, Charges Wealthy Nigerians To Advance Humanity

 Metro4 days ago
Metro4 days agoWhy We Killed Ogun FRSC Officer, Daughter — Suspect Manfriend, Herbalists

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoJUST IN: CBN Removes Cash Deposit Limits, Raises Weekly Withdrawal To N500,000

 News3 days ago
News3 days ago9 Common Resume Mistakes Graduates Make – And How To Avoid Them

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoKingsley Aigbangbee: A Name Built On Grassroots Impact

 Entertainment3 days ago
Entertainment3 days agoIt Is Getting Out Of Hand – Tuface Cries Out Amid Marital Crisis

 Headline4 days ago
Headline4 days agoUS Imposes Visa Restrictions On Nigerians Linked To Religious Freedom Violations

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoOba Of Benin Suspends Priest, Reaffirms Appointment Of Okao




















