Headline
Tracing Putin’s 25-year Reign As Russians Vote
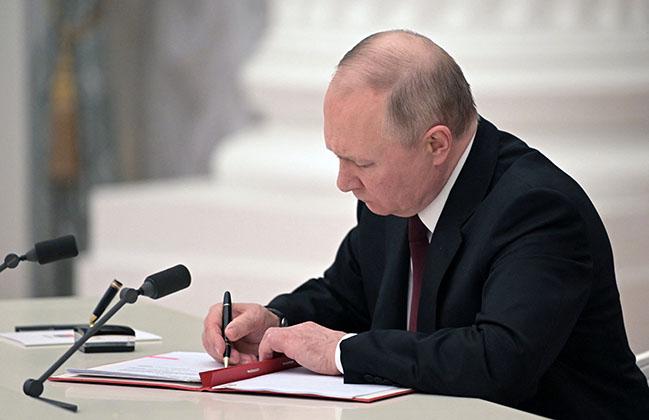

The voting process in Russia is ongoing, with incumbent President Vladimir Putin widely anticipated to secure his fifth term as the country’s leader.
Putin is running as an independent candidate.
According to Al Jazeera, other candidates are perceived as “figureheads” and included in the process solely to show Putin’s popularity.
The three-day voting started on Friday, March 15, 2024.
However, based on the 2020 constitutional amendment that invalidated his previous terms, the upcoming March 15–17 election will be considered his first one.
112 million people aged 18 and above in Russia are eligible to vote.
People in annexed Crimea and occupied parts of Ukraine will also vote.
Putin has served four terms.
If he wins, the 71-year-old is anticipated to hold power for an additional six years, courtesy of the 2020 constitutional amendment.
Putin, born on October 7, 1952 in Leningrad, Russia, is a Russian intelligence officer and politician.
He held the position of President of Russia from 1999 to 2008 and again from 2012 onwards.
Additionally, he has also served as the country’s prime minister in 1999 and from 2008 to 2012.
READ ALSO: Putin To Run Again For President In 2024
Below is a timeline of Putin’s 25 years as a leader of the Eastern Europe federation:
Putin has an extensive background in foreign intelligence, having spent 15 years working for the KGB (Committee for State Security).
Shortly after, Putin began working as an advisor to Sobchak, who was the first democratically elected mayor of St. Petersburg.
By 1994, he had ascended to the position of first deputy mayor.
In 1996, Putin relocated to Moscow and became a part of the presidential staff, serving as the deputy to Pavel Borodin, the chief administrator of the Kremlin (The Kremlin is a fortified complex located in Moscow, Russia.
It serves as the official residence and workplace of the President of Russia. It is located at the heart of Russian political power and government).
In July 1998, President Boris Yeltsin appointed Putin as the director of the Federal Security Service
Shortly after, Putin assumed the role of secretary of the influential Security Council.
Yeltsin, in his quest for a successor to carry on his legacy, selected Putin as prime minister in 1999.
As reported by Voice of America, Yeltsin said in a televised speech on August 9, 1999, “I have decided to now name the person who is, in my opinion, able to consolidate society and, drawing support from the broadest political forces, to ensure the continuation of reforms in Russia.
“He will be able to unite around himself those who are to renew Great Russia in the new 21st century.”
READ ALSO: Putin Revokes Russia’s Ratification Of Nuclear Test Ban Treaty
According to Britannica, Putin’s public approval ratings experienced a significant boost when he successfully executed a highly organised military operation against secessionist rebels in Chechnya, despite his previous lack of recognition.
Tired of Yeltsin’s unpredictable actions, the Russian public admired Putin’s calmness and resolute nature in challenging situations, as per Britannica.
Putin’s backing of the new electoral bloc, Unity, played a crucial role in securing its triumph in the December parliamentary elections.
Yeltsin made the unexpected decision to step down on December 31, 1999, appointing Putin as the acting president.
Putin secured a decisive victory in the March 2000 elections, garnering approximately 53 per cent of the vote.
Putin was reelected in March 2004 after overseeing an economy that experienced growth following a prolonged recession in the 1990s.
In the December 2007 parliamentary elections, United Russia, Putin’s party, secured a significant majority of seats.
In 2008, Putin selected Dmitry Medvedev as his successor due to a constitutional provision that required him to step down.
Shortly after Medvedev’s victory in the March 2008 presidential election, Putin announced that he would be assuming the role of chairman of the United Russia party.
As anticipated, Medvedev wasted no time in nominating Putin as the country’s prime minister shortly after assuming office on May 7, 2008. The appointment was confirmed by Russia’s parliament the next day.
READ ALSO: Putin Says Zelensky A ‘Disgrace To Jewish People’
In September 2011, Medvedev announced that he and Putin would switch positions.
This decision put an end to the speculation about Medvedev running for a second term.
On March 4, 2012, Putin was elected to a third term as Russia’s president.
Prior to his inauguration, Putin stepped down as United Russia chairman, transferring control of the party to Medvedev.
On May 7, 2012, he took office as president and nominated Medvedev as prime minister.
On March 18, 2018, Putin secured a significant majority of the vote in an election that marked the beginning of his fourth term.
In January 2020, Putin announced his intention to bring about modifications that would eliminate term limits for presidents.
Medvedev promptly resigned as prime minister.
Putin signed the law that could extend his time in office until 2036, allowing him to run for the presidency twice more in his lifetime.
According to The Guardian UK, officially, the new law limits Russian citizens to two presidential terms in their lifetime.
It also outlawed the shuffling between the presidency and the role of prime minister that Putin employed earlier in his career.
However, according to the law, terms served before it entered into force are not counted. This means that Putin’s previous four terms, including the current one, are not considered, allowing him to potentially serve two more terms.
If he holds onto power until 2036, his time in office will exceed even that of Joseph Stalin, who governed the Soviet Union for 29 years.
This would make Putin the longest-serving leader in Moscow since the days of the Russian empire.
Headline
UK Supported US Mission To Seize Russian-flagged Oil Tanker – Defense Ministry
The British Ministry of Defence said on Wednesday that it provided support to the United States in its operation to seize a Russian-flagged oil tanker in the North Atlantic.
US seized the tanker, which was being shadowed by a Russian submarine on Wednesday, after pursuing it for more than two weeks across the Atlantic as part of Washington’s efforts to block Venezuelan oil exports.
According to Britain, its armed forces gave pre-planned operational support, including basing following a US request for assistance.
READ ALSO:UK Introduces Powers To Seize Phones, SIM Cards From Illegal Migrants
The UK also said a military vessel provided support for the US forces pursuing the tanker, and the Royal Air Force provided surveillance support from the air.
Defence Secretary John Healey stated that the operation targeted a vessel with a nefarious history linked to Russian and Iranian sanctions evasion networks.
“This action formed part of global efforts to crack down on sanctions busting,” he said in a statement.
READ ALSO:Venezuelan Deportees: US Embassy Gives Reason For Reducing Visa Validity For Nigerians
According to him, the US was Britain’s closest defence and security partner.
“The depth of our defence relationship with the US is an essential part of our security, and today’s seamlessly executed operation shows just how well this works in practice,” he added.
The British government said that the Bella-1 tanker, now renamed Marinera, is sanctioned by the US under its counter-Iran sanctions,
The MoD statement said the support was provided in full compliance with international law.
Headline
Russia Deploys Navy To Guard Venezuelan Oil Tanker Chased By US In Atlantic
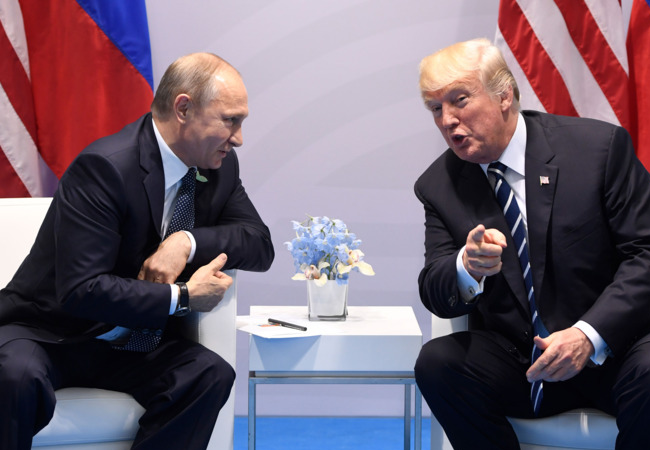

Russia has deployed naval assets to escort a sanctioned oil tanker across the Atlantic following reported moves by the United States to seize the vessel.
US forces were said to be preparing to board the ship, which has a history of transporting Venezuelan crude oil and was last believed to be sailing between Scotland and Iceland.
CBS News reported that Russia stepped in to protect the tanker, raising the prospect of a direct confrontation between the two powers at sea.
READ ALSO:Russia Calls up 135,000 Military Personnel
By sending naval ships into the North Atlantic, Russian President Vladimir Putin is signalling to United States President Donald Trump that any US action would carry consequences, coming after the US president threatened that he might use the military to seize Greenland.
The tanker, currently empty, previously operated under the name Bella 1. Last month, the US Coast Guard attempted to board it in the Caribbean with a warrant over alleged breaches of US sanctions and claims that it had shipped Iranian oil.
The vessel later changed course, renamed itself Marinera and reportedly reflagged from Guyana to Russia.
READ ALSO:Venezuela Frees Eight Opposition Leaders
Trump last month said he had ordered a ‘blockade’ of sanctioned oil tankers entering and leaving Venezuela, a policy the government in Caracas branded ‘theft’.
Ahead of the US seizure of ousted Venezuelan leader Nicolás Maduro on Saturday, Trump accused the country’s government of using ships to smuggle drugs into the United States.
Two US officials told CBS News on Tuesday that American forces were planning to board the Marinera, adding that Washington would prefer to seize the tanker rather than sink it.
Russia’s Foreign Ministry said it expects Western countries to respect principles of freedom of navigation.
(Daily Mail News)
Headline
UK Introduces Powers To Seize Phones, SIM Cards From Illegal Migrants

The United Kingdom has rolled out expanded enforcement powers allowing authorities to confiscate mobile phones and SIM cards from migrants who enter the country illegally.
The new measures, which do not require an arrest, came into force on Monday at the Manston migrant processing centre in Kent and represent a significant tightening of border controls.
According to the Home Office, the powers are intended to support intelligence-gathering operations aimed at disrupting criminal networks that organise and profit from dangerous Channel crossings.
Officials at the centre are equipped with technology that enables them to extract and analyse data from seized devices, a move the government says will help track and dismantle smuggling rings.
READ ALSO:Russia-Ukraine War: Pope Leo Calls For Global Christmas Truce
Under the revised rules, migrants are permitted to be asked to remove outer garments if there is suspicion that phones are being concealed.
In certain circumstances, officers may also check mouths for hidden SIM cards or small electronic items.
The National Crime Agency said information recovered from devices could accelerate investigations and improve the effectiveness of action against organised crime groups.
Border Security Minister Alex Norris said the policy was necessary to regain control of the UK’s borders and confront human trafficking operations.
“We are committed to restoring order and tackling the people-smuggling gangs behind this lethal trade,” Norris said.
READ ALSO:
“These stronger laws give authorities the tools to disrupt, intercept and dismantle these networks more quickly and effectively,” he added.
The legislation also introduces tougher criminal penalties linked to illegal crossings.
Individuals found storing or supplying boat engines for unauthorised journeys could face prison terms of up to 14 years, while those involved in researching equipment or plotting routes may be liable to sentences of up to five years.
Government officials stressed that the powers would be exercised with discretion.
READ ALSO:UK Unveils Record-breaking Bid For 2035 Women’s World Cup
The Minister for Migration and Citizenship, Mike Tapp, said devices could be returned depending on individual circumstances and the relevance of the information obtained.
“If a device may contain intelligence that helps combat smuggling, it is right that it can be seized,” Tapp said, adding that the approach would not undermine compassion toward migrants.
However, humanitarian organisations have expressed unease about the impact of the policy.
The Refugee Council warned that mobile phones often serve as vital lifelines for migrants, enabling contact with family members and access to support services, and urged authorities to ensure the measures are applied in a proportionate and humane manner.

 News3 days ago
News3 days agoWhat I Saw After A Lady Undressed Herself — Pastor Adeboye

 Headline3 days ago
Headline3 days agoPROPHECY: Primate Ayodele Reveals Trump’s Plot Against Tinubu

 Metro3 days ago
Metro3 days agoArmed Robbers Shot PoS Operator To Death In Edo

 Metro2 days ago
Metro2 days agoAAU Disowns Students Over Protest

 Metro2 days ago
Metro2 days agoNine Soldiers Feared Dead In Borno IED Explosion

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoNNPCL Reduces Fuel Price Again

 Metro2 days ago
Metro2 days agoEdo: Suspected Kidnappers Kill Victim, Hold On To Elder Brother

 Metro3 days ago
Metro3 days agoJoint Task Force Kills 23 Bandits Fleeing Kano After Attacks

 Entertainment3 days ago
Entertainment3 days agoPHOTOS: Anthony Joshua Makes First Social Media Post After Surviving Deadly Car Crash

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days ago2027: Rivers APC Pledges To Follow Wike’s Instructions






























