Health
COVID-19: Edo Clears 917 Suspected Cases, Intensifies 830 Contacts Tracing
Published
5 years agoon
By
Editor
Edo State government says it has cleared and exited 917 suspected cases of COVID-19 across the state who have completed the compulsory 14-day follow up and tested negative.
The state government also disclosed that contact tracing of over 830 suspected cases is currently ongoing across the 192 wards of the state.
The state’s Commissioner for Health, Dr. Patrick Okundia, while disclosing this in Benin said the cleared cases comprise 338 Persons of Interests (POI) and 579 others that had various degrees of contacts with confirmed cases.
READ ALSO: Just In: Another COVID-19 Loophole Bursted In Edo
According to him, the state has tested over 917 residents, screened over 126, 000 persons.
The Commissioner further disclosed that the state has so far recorded 95 confirmed cases, 885 suspected cases, 5 deaths and 35 discharges.
He noted that the state’s improved efforts at screening and testing were responsible for the rising number of confirmed cases.
READ ALSO: COVID-19: Edo Discharges 20 Patients
The commissioner, however, identified screening and testing as essential in the government’s efforts at containing the pandemic.
He said, “The Edo State Government encourages all residents with symptoms of the disease to come out for screening, testing and treatment as early detection is key to containing the virus. When detected early, a patient’s chance for survival increases.
“We urge you to comply with all government directives, aimed at ensuring the health and safety of all Edo people. While the government ramps up efforts to win the war against this common enemy, it is imperative that residents stay at home and observe social distancing guidelines and other precautionary measures against the spread of the disease, including regular handwashing with soap under running water and the use alcohol-based hand sanitisers. Cover your mouth and nose properly when sneezing and/or coughing. Also do well to report anyone with oversea travel history.”
READ ALSO: Oba Of Benin Welcomes New Baby
Okundia, however, reassured that the remaining 55 cases that are yet to be discharged are on active treatment at various isolation centres in the state and are responding well to treatment.
PHOTO: File
You may like
Health
LASG FLags Off Polio Outbreak Response Campaign
Published
5 months agoon
January 20, 2025By
Editor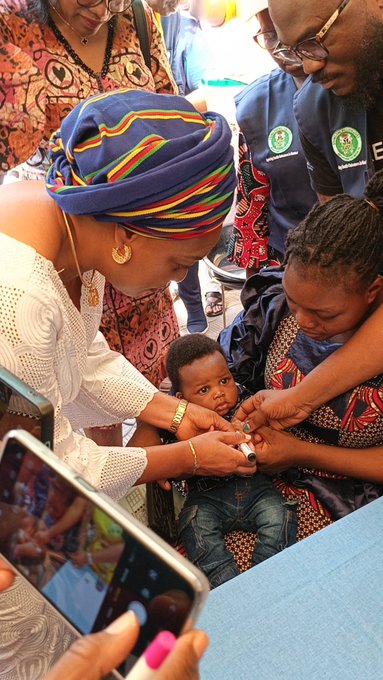
The Lagos State Government, through the Lagos State Primary Health Care Board, has launched the 2025 Polio Outbreak Response Campaign, reaffirming its commitment to eradicating polio and safeguarding the health of its children.
The ceremony, held at the Simpson Primary Healthcare Centre, was led by the First Lady of Lagos State, Dr. (Mrs.) Claudiana Ibijoke Sanwo-Olu, represented by Mrs. Widad Jumoke Mustafa, a member of the Committee of Wives of Lagos State Officials (COWLSO).
In her address, the First Lady emphasised the state government’s proactive measures to keep Lagos polio-free, highlighting the critical importance of the campaign in preventing the debilitating effects of poliomyelitis, which can result in paralysis or death.
READ ALSO: IMPEACHMENT: Lagos Ex-Speaker, Obasa’s ‘Sins’ Revealed
The First Lady also called on parents, community leaders, and stakeholders to support the campaign by ensuring eligible children are vaccinated.
Targeting children aged 0-59 months, vaccination teams will administer the Oral Polio Vaccine (OPV) to prevent virus transmission.
Dr. Kemi Ogunyemi, the Special Adviser on Health, expressed gratitude to Lagosians for their continued cooperation in the fight against polio. While appreciating all healthcare workers and partners for their services, Mrs. Ogunyemi encouraged parents to present their children and wards for the exercise.
Also speaking, the Chairman of Lagos Mainland Local Government, Mrs. Omolola Rashidat Essien opined that Immunization is key in ensuring that children are kept safe from polio and other vaccine preventable diseases.
Dr. Abimbola Bowale, the Supervising Permanent Secretary, Lagos State Primary Health Care Board, who also spoke at the event, underscored the life-saving importance of immunization.
“All children aged 0-59 months need multiple doses of the polio vaccine to ensure full protection. Any child missed represents a potential risk for the poliovirus to spread. The vaccine is safe, effective, and crucial in keeping our communities polio-free,” he stated.
Dr. Bowale also outlined several strategies to ensure the success of the campaign, including fixed post teams stationed at primary healthcare centres and public health facilities, house-to-house visits, and a transit strategy to reach special locations such as places of worship, schools, motor parks, and other public venues.
The event concluded with Dr. (Mrs.) Claudiana Ibijoke Sanwo-Olu officially launched the campaign, marking a renewed effort to maintain Lagos State’s polio-free status.
The Lagos state suspected cholera cases have risen to 421.
The Commissioner for Health, Akin Abayomi disclosed this on his Instagram handle @profakinabayomi on Saturday.
“As of June 20, 2024, an additional four suspected cholera cases have been reported, as illustrated in the accompanying graph,” he wrote.
He noted that the Emergency Operations Centre in collaboration with all relevant partners is actively engaged in contact tracing, community-based surveillance, awareness campaigns, sample testing, and ensuring that confirmed cholera cases receive appropriate medical treatment.
READ ALSO: Two Suspects Arrested For Stealing Car From Mosque During Juma’at Prayer
On Friday, the commissioner confirmed 35 cases out of the 417 suspected cases and 24 deaths across 20 Local Government Areas in the state.
The cases were reported from Agege, Badagry, Ikeja, Mushin, Ajeromi-Ifelofun, Epe, Ikorodu, Ojo, Alimosho, and Eti-Osa.
Others were Kosofe, Oshodi-Isolo, Amuwo-Odofin, Ibeju-Lekki, Lagos Island, Shomolu, Apapa, Ifako-Ijaiye, Lagos mainland, and Surulere.
Cholera is a food and water-borne disease caused by ingesting the bacteria— Vibrio cholerae — in contaminated water and food. Cholera can cause severe acute watery diarrhoea, and the severe forms of the disease can kill within hours if left untreated.
In Nigeria, cholera is an endemic and seasonal disease, occurring annually mostly during the rainy season and more frequently in areas with poor sanitation.
READ ALSO: Police Arrest 28yr Old Suspected Cultists, Recover Gun In Delta Community
The World Health Organisation on Thursday announced a spike in cholera in several regions of the world, with almost 195,000 cases and over 1,900 deaths reported in 24 countries since the start of 2024.
WHO said the Eastern Mediterranean Region reported the highest number of cases, followed by the African Region, the Region of the Americas, the Southeast Asia Region, and the European Region.
The global health body, however, noted that there are no reported cases in the Western Region, according to its bulletin released on Wednesday.
It said it exhausted its global stockpile of Oral Cholera Vaccines by March but was able to exceed “the emergency target of five million doses in early June for the first time in 2024.”

By Silver Yeibake
Autism, commonly known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects communication, social interaction, and behavior. Autism is referred to as a spectrum condition since it can manifest in a variety of symptoms and abilities. While the actual cause of autism is unknown, evidence suggests that genetic and environmental factors interact to influence its development.
The risk factors include a sibling with autism, advanced age of parents, exposure to certain air pollutants and pesticides before birth, extreme prematurity, mothers with diabetes, immune system disorders or obesity, any difficulty with delivery leading to deprivation of oxygen to the baby’s brain, fever during pregnancy, lack of certain vitamins minerals during pregnancy, and certain genetic conditions, such as Down, fragile X, and Rett syndromes.
“Risk factors can not on their own cause a disease. However, they can increase the likelihood of that disease in a person.”
It is important to know that contrary to trending claims online, there is no scientific or medical evidence that vaccines or consumption of sugar are risk factors for autism.
READ ALSO: Kidney Stones: What You Need To Know
Autism is defined by difficulties in social interaction and communication. Individuals with autism may struggle to grasp social cues, maintain eye contact, and engage in typical back-and-forth conversations. Some people may also engage in meaningless, repetitive actions, such as hand-flapping or rocking, and have strong interests in specific areas.
It is essential to remember that autism is a lifelong diagnosis, but with early intervention and adequate care, people with autism can live fulfilling lives.
Autism treatment frequently includes behavioral therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training. Each individual with autism is unique, thus interventions should be tailored to meet their personal needs and strengths.
In spite of the difficulties that autism can cause, many people with autism possess unique talents and abilities. Some people may succeed in fields such as music, art, mathematics, or programming, thus it is important for society to acknowledge and honor the qualities and achievements of people with autism.
In summary, autism is a complicated and diverse disorder that affects individuals in various ways. By raising autism knowledge, understanding, and acceptance, we can build a more inclusive society in which people with autism can thrive and attain their full potential.
Dr. Yeibake, Weriwoyingipre Silver.
Senior Registrar,
Faculty Of Pediatrics,
WACP
- NYSC Commends Bauchi Govt On Infrastructural Development In Orientation Camp
- Gunmen Kill 10 In Anambra Community
- EFCC Arrests 31 Suspected Internet Fraudsters In Nasarawa
- 30-year-old Man Hacks Mother To Death
- FCT Police Arrest Three Wanted Kidnappers
- Ghana Deports Convicted Nigerian For Smuggling Fake $100,000
- Man Jailed Seven Years For N11.4m Enugu Land Fraud
- Tragedy As 23-year-old Dies By Self-stabbing In Delta
- Police Raid Criminal Hideouts In Delta, Arrest Suspects, Seize Weapons
- Sex Worker Dies After Dispute Over N15,000 Refund In Ondo
About Us
Trending

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoArson: Man To Pay N150m For Burning FRSC Patrol Vehicle In Bauchi

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days agoBREAKING: Confusion As APC Chair, Ganduje Resigns

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoAuchi Poly Mass Comm Class of 2006 Holds Maiden Reunion in Benin

 Politics4 days ago
Politics4 days ago‘Peace Has Returned To Rivers’ — Wike, Fubara Speak After Meeting Tinubu

 Headline2 days ago
Headline2 days ago‘They Checked My Instagram’ – Nigerian Lady Breaks Down After Landing In U.S, Denied Entry

 Metro1 day ago
Metro1 day agoBREAKING: Emir’s Palace, NDLEA Office Set Ablaze As Protest Rocks Kwara

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoNSCDC, Immigration, Others: FG Postpones Recruitment, Changes Portal

 Metro4 days ago
Metro4 days agoNAPTIP Declares Speed Darlington Wanted For Tape, Cyberbullying

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoChelsea Set To Offload Jackson, Madueke, 8 Others [See list]

 Metro1 day ago
Metro1 day agoPanic As Bees Invade Central Mosque In Edo

















